Home | Glossary | Resources | Help | Contact Us | Course Map
Archival Notice
This is an archive page that is no longer being updated. It may contain outdated information and links may no longer function as originally intended.
Time Required to Perform Laboratory Analysis
Step 3: DNA Analysis, Extraction
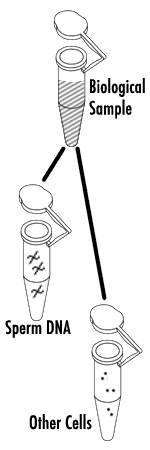
Extraction is the process of removing DNA from a stain and, if necessary, removing residual stain material from the DNA. If the stain is identified as semen, additional extraction steps are required to separate sperm cells from the other cells in the stain. Sperm separation doubles the time required for the extraction process and creates two independent subsamples that are carried through all subsequent processes. The first subsample is predominantly composed of sperm DNA, while the second subsample is from other cells. In a sexual assault case, this technique allows the separation of DNA from the male and female components. In most casework analyses, it is important to determine the amount of sperm and non-sperm DNA present in the extract.
See the YouTube Terms of Service and Google Privacy Policy
Additional Online Courses
- What Every First Responding Officer Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Collecting DNA Evidence at Property Crime Scenes
- DNA – A Prosecutor’s Practice Notebook
- Crime Scene and DNA Basics
- Laboratory Safety Programs
- DNA Amplification
- Population Genetics and Statistics
- Non-STR DNA Markers: SNPs, Y-STRs, LCN and mtDNA
- Firearms Examiner Training
- Forensic DNA Education for Law Enforcement Decisionmakers
- What Every Investigator and Evidence Technician Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Principles of Forensic DNA for Officers of the Court
- Law 101: Legal Guide for the Forensic Expert
- Laboratory Orientation and Testing of Body Fluids and Tissues
- DNA Extraction and Quantitation
- STR Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Communication Skills, Report Writing, and Courtroom Testimony
- Español for Law Enforcement
- Amplified DNA Product Separation for Forensic Analysts