Archival Notice
This is an archive page that is no longer being updated. It may contain outdated information and links may no longer function as originally intended.
Home | Glossary | Resources | Help | Contact Us | Course Map
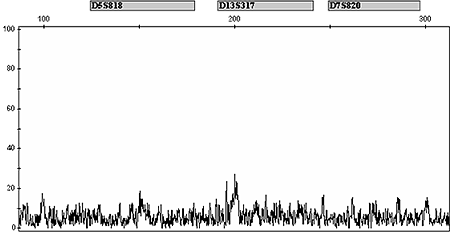
Noise describes a series of non-reproducible background peaks that occur along the baseline in all samples. A wide variety of factors, including amplified current fluctuations within the electronic circuitry, air bubbles, urea crystals, and sample contamination, can create noise. If large enough (close to the laboratory threshold), they may be confused with an allele or mask alleles.
Trained analysts using a proper analytical threshold should not have difficulty differentiating actual alleles with noise and vice versa; they should be familiar with the signal-to-noise ratio of the instrument and/or the specific data. If unsure, data interpretation may involve viewing both raw and analyzed data to assess the signal-to-noise ratio and distinguish real data from noise. Noise is not reproducible; one way to differentiate alleles from noise is to rerun the sample.
Additional Online Courses
- What Every First Responding Officer Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Collecting DNA Evidence at Property Crime Scenes
- DNA – A Prosecutor’s Practice Notebook
- Crime Scene and DNA Basics
- Laboratory Safety Programs
- DNA Amplification
- Population Genetics and Statistics
- Non-STR DNA Markers: SNPs, Y-STRs, LCN and mtDNA
- Firearms Examiner Training
- Forensic DNA Education for Law Enforcement Decisionmakers
- What Every Investigator and Evidence Technician Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Principles of Forensic DNA for Officers of the Court
- Law 101: Legal Guide for the Forensic Expert
- Laboratory Orientation and Testing of Body Fluids and Tissues
- DNA Extraction and Quantitation
- STR Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Communication Skills, Report Writing, and Courtroom Testimony
- Español for Law Enforcement
- Amplified DNA Product Separation for Forensic Analysts