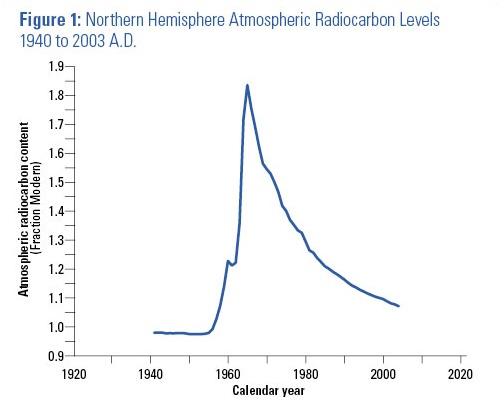
Figure 1: Northern Hemisphere Atmospheric Radiocarbon Levels 1940 to 2003 A.D.
From the article National Institute of Justice, "What Is Carbon Dating?," March 25, 2012.
As a result of above-ground nuclear weapons testing in the 1950s and 1960s, atmospheric radiocarbon levels increased dramatically. Atmospheric radiocarbon levels have been declining since the Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty of 1963 went into effect. Using 1.0 Fraction Modern (FM) as a representation of the level of atmospheric radiocarbon in 1950, the atmospheric radiocarbon concentration in 1940 was 0.98 FM. It rose rapidly in the 1950s and early 1960s and peaked at 1.83 FM in 1963. By 2003 the level of atmospheric radiocarbon had dropped to 1.07 FM. The rapid rise and subsequent decline of atmospheric radiocarbon concentrations is referred to as the "bomb spike."