Aviso de archivo
Esta es una página de archivo que ya no se actualiza. Puede contener información desactualizada y es posible que los enlaces ya no funcionen como se pretendía originalmente.
Home | Glossary | Resources | Help | Contact Us | Course Map
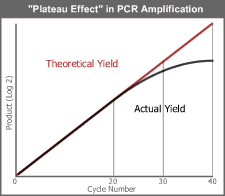
The term plateau effect is used to describe the attenuation of the normally exponential rate of product accumulation in PCR. The attenuation occurs during the late PCR cycles when the accumulation of product reaches 0.3 to 1 picomole. Depending on reaction conditions and thermal cycling, one or more of the following may influence when the plateau is reached:
- Depletion of substrates (dNTPs or primers)
- Stability of the reactants (dNTPs or enzyme) particularly at the denaturation temperature
- End-product inhibition (pyrophosphate, duplex DNA)
- Competition for reactants by nonspecific products or primer-dimer
- Reannealing of specific product at concentration above 10-8 M (may decrease the extension rate or processivity of Taq DNA polymerase or change branch-migration of product strands and displacement of primers)
- Incomplete denaturation/strand separation of product at high product concentration11
An important consequence of reaching plateau is that nonspecific products resulting from mispriming events, initially present at low concentration, may continue to amplify preferentially. Optimizing the number of PCR cycles is the best way to avoid amplifying background products.
Summary
PCR yield is directly affected by the primer design. There are commercially available primer design software packages that are commonly used to assist scientists in designing primers.
Read about primer design software packages at the Chemical Science and Technology home page of NIST.
Additional Online Courses
- What Every First Responding Officer Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Collecting DNA Evidence at Property Crime Scenes
- DNA – A Prosecutor’s Practice Notebook
- Crime Scene and DNA Basics
- Laboratory Safety Programs
- DNA Amplification
- Population Genetics and Statistics
- Non-STR DNA Markers: SNPs, Y-STRs, LCN and mtDNA
- Firearms Examiner Training
- Forensic DNA Education for Law Enforcement Decisionmakers
- What Every Investigator and Evidence Technician Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Principles of Forensic DNA for Officers of the Court
- Law 101: Legal Guide for the Forensic Expert
- Laboratory Orientation and Testing of Body Fluids and Tissues
- DNA Extraction and Quantitation
- STR Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Communication Skills, Report Writing, and Courtroom Testimony
- Español for Law Enforcement
- Amplified DNA Product Separation for Forensic Analysts