Home | Glossary | Resources | Help | Contact Us | Course Map
Aviso de archivo
Esta es una página de archivo que ya no se actualiza. Puede contener información desactualizada y es posible que los enlaces ya no funcionen como se pretendía originalmente.
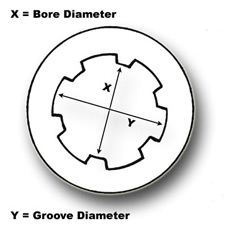
Caliber/Diameter
The bore diameter of the barrel of a rifled firearm is defined as the diameter of the circle formed by the tops of the lands inside the barrel. This diameter does not include the grooves within the barrel. However, a portion of the mass of a fired bullet is extruded into these grooves. Therefore, the diameter of a fired bullet will approximate the larger groove diameter and will always be greater than the bore diameter of the firearm.
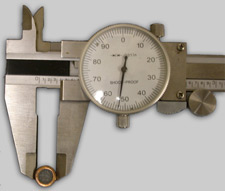
The measured diameter of fired bullets is taken from one groove impression (a high point on a fired bullet) to a groove impression on the opposite side of the bearing surface. If there are an odd number of groove impressions, the measurement is taken from the edges of a pair of impressions. The base of the bearing surface of a bullet is used because it is generally more protected when a bullet impacts with an object. Often the bearing surface endsat the base of the entire bullet, althoughwith boattailed bullets this would not be the case. For bullets that are severely flattened or distorted, it may be possible to measure the circumference and calculate an approximate diameter.
Whenever measurements are taken, avoid damaging or obliterating microscopic marks on the groove impressions with measuring instruments such as calipers. Plastic calipers can minimize this potential problem.
In the following situations, a measurement should be taken at an alternate location:
- Significant base mutilation upon impact, altering the width or apparent caliber
- Unusual amount of base expansion after firing (e.g., deep hollow-based lead bullets)
- Unusual base expansion of lead bullets after firing from a short-barreled handgun
Possible Cartridge Types
In the following chart, the measured diameter of a bullet in inches corresponds to possible cartridge type(s).
| Possible Cartridge Types Indicated Based on the Measured Diameter of a Fired Bullet | |
| DIAMETER OF FIRED BULLET * | POSSIBLE CALIBERS |
| .202" - .228" | 22 5.5mm 5.56mm |
| .247" - .271" | 25 Auto 6.35mm |
| .302" - .328" |
32 Auto |
| .353 " - .373" | .357 Mag. 38 Spl. 380 Auto 9mm (various types) |
| .401" - .410" | 40 S&W 41 Rem Mag 10mm Auto |
| .425" - .431" | 44 Rem. Mag. |
| .447" - .458" | 45 Auto 45 Colt 455 Webley/Colt |
| * assumes little or no deformation that makes measurement difficult | |
Measured caliber/diameter, as with other physical features, is only one factor to consider. A bullet of a given caliber may be consistent with any number of cartridge types.
Additional Online Courses
- What Every First Responding Officer Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Collecting DNA Evidence at Property Crime Scenes
- DNA – A Prosecutor’s Practice Notebook
- Crime Scene and DNA Basics
- Laboratory Safety Programs
- DNA Amplification
- Population Genetics and Statistics
- Non-STR DNA Markers: SNPs, Y-STRs, LCN and mtDNA
- Firearms Examiner Training
- Forensic DNA Education for Law Enforcement Decisionmakers
- What Every Investigator and Evidence Technician Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Principles of Forensic DNA for Officers of the Court
- Law 101: Legal Guide for the Forensic Expert
- Laboratory Orientation and Testing of Body Fluids and Tissues
- DNA Extraction and Quantitation
- STR Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Communication Skills, Report Writing, and Courtroom Testimony
- Español for Law Enforcement
- Amplified DNA Product Separation for Forensic Analysts