Aviso de archivo
Esta es una página de archivo que ya no se actualiza. Puede contener información desactualizada y es posible que los enlaces ya no funcionen como se pretendía originalmente.
Home | Glossary | Resources | Help | Contact Us | Course Map
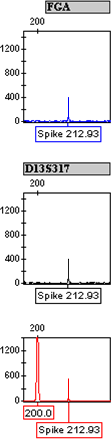
Spikes are narrow peaks usually attributed to fluctuation in voltage or the presence of minute air bubbles in the capillary. Spikes can also be caused by crystals in the polymer and/or fluorescent material in the polymer or formamide. Spikes, unlike other artifacts, are generally seen in the same position in all colors. However, it is possible to detect spikes in a single color.
Analysts should view both the raw and analyzed data for each sample. The raw data produce a non-filtered view of the sample run, while analyzed data can obscure detection of a spike. Frequently, spikes are more readily detected in raw data versus analyzed data. The analyzed data provide an exact data point and base pair size for each peak. Spikes that are not obscured in the analyzed data can be assigned an exact data point for each color displayed.
The occurrence of spikes can be minimized by following the instrument manufacturer's procedures for reagent and sample handling. If spikes persist, analysts may need to contact the manufacturer. Frequent electronic spiking can occur due to poorly functioning instruments.
Additional Online Courses
- What Every First Responding Officer Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Collecting DNA Evidence at Property Crime Scenes
- DNA – A Prosecutor’s Practice Notebook
- Crime Scene and DNA Basics
- Laboratory Safety Programs
- DNA Amplification
- Population Genetics and Statistics
- Non-STR DNA Markers: SNPs, Y-STRs, LCN and mtDNA
- Firearms Examiner Training
- Forensic DNA Education for Law Enforcement Decisionmakers
- What Every Investigator and Evidence Technician Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Principles of Forensic DNA for Officers of the Court
- Law 101: Legal Guide for the Forensic Expert
- Laboratory Orientation and Testing of Body Fluids and Tissues
- DNA Extraction and Quantitation
- STR Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Communication Skills, Report Writing, and Courtroom Testimony
- Español for Law Enforcement
- Amplified DNA Product Separation for Forensic Analysts