Aviso de archivo
Esta es una página de archivo que ya no se actualiza. Puede contener información desactualizada y es posible que los enlaces ya no funcionen como se pretendía originalmente.
Home | Glossary | Resources | Help | Contact Us | Course Map
The DNA analysis described thus far has been based on the genetic profiling of nuclear DNA (nDNA), i.e., DNA found in the nucleus of a cell. Another method of DNA typing admitted in some criminal cases for DNA evidence sample comparison is Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). MtDNA is found in the mitochondria of a cell, outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. The mitochondria are the energy source for a cell. MtDNA has 16,569 base pairs and possesses 37 genes.1 The portion that is used for analysis is a "non-coding control region, also known as the D-loop, that exhibits a fair degree of variation between individuals and is therefore useful for human identity testing purposes". MtDNA, like nDNA, can be located, extracted and copied using amplification by the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
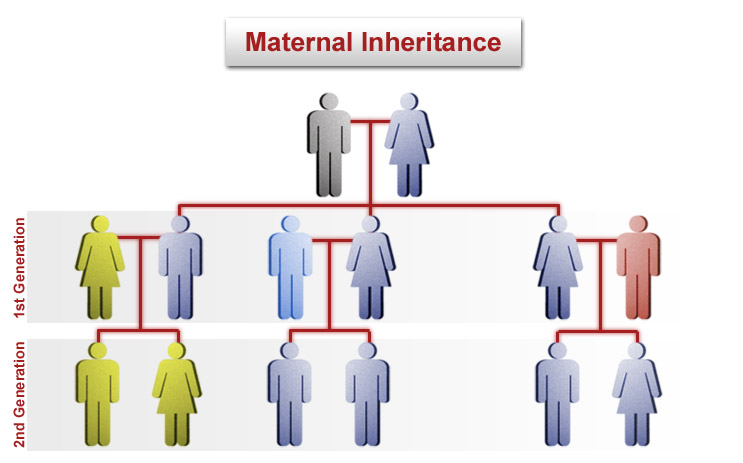
MtDNA is maternally inherited. Thus maternally related individuals will share mtDNA types and may be used to obtain a reference sample. Daughters pass on to their children the same mtDNA profile they inherited from their own mothers whereas sons do not pass on the mtDNA profile. MtDNA can be extracted from much smaller sample than that required for a nDNA extraction.
Additional Online Courses
- What Every First Responding Officer Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Collecting DNA Evidence at Property Crime Scenes
- DNA – A Prosecutor’s Practice Notebook
- Crime Scene and DNA Basics
- Laboratory Safety Programs
- DNA Amplification
- Population Genetics and Statistics
- Non-STR DNA Markers: SNPs, Y-STRs, LCN and mtDNA
- Firearms Examiner Training
- Forensic DNA Education for Law Enforcement Decisionmakers
- What Every Investigator and Evidence Technician Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Principles of Forensic DNA for Officers of the Court
- Law 101: Legal Guide for the Forensic Expert
- Laboratory Orientation and Testing of Body Fluids and Tissues
- DNA Extraction and Quantitation
- STR Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Communication Skills, Report Writing, and Courtroom Testimony
- Español for Law Enforcement
- Amplified DNA Product Separation for Forensic Analysts