Home | Glossary | Resources | Help | Contact Us | Course Map
Aviso de archivo
Esta es una página de archivo que ya no se actualiza. Puede contener información desactualizada y es posible que los enlaces ya no funcionen como se pretendía originalmente.
Types of Evidence
Several types of evidence may be found at a crime scene. This module presents a brief description of some of the general evidence categories. Evidence related to firearms and toolmarks, as well as the collection and handling of these types of evidence, are covered in depth.
The types of evidence discussed in this module include the following:
- Physical
- Biological
- Drug
- Other
Physical Evidence
Physical evidence refers to a wide range of physical objects (often minute in size).
Examples of physical evidence include
- firearms and fired ammunition,
- fingerprints,
- toolmarks, tire tracks, and footwear impressions,
- hairs, fibers, glass, paint, and other trace evidence.
Physical evidence may be considered as
- corroborative evidence, which tends to confirm or support the theory of the crime,
- circumstantial evidence, which indirectly infers a particular conclusion regarding the crime.
Trace Evidence
Trace evidence is a subtle category of physical evidence that is minute and transient, but measurable. Typically, this evidence does not appear until larger items of physical evidence are subjected to closer examination in the laboratory. A microscope with good illumination or other instrumentation may be required to detect the presence of trace evidence.
The importance of trace evidence cannot be overemphasized. Awareness of this type of evidence can be critical to an investigation; training and experience are essential to maximize the value of this type of physical evidence.
Photographing the area where the evidence is collected not only provides documentation of the collection but also assists in locating trace evidence.
Even if identification cannot be made in the laboratory, the investigator and prosecutor may use trace evidence as part of a convincing circumstantial case. Successfully presenting trace evidence in the courtroom requires additional skill and effort during collection, testing, and case preparation.
Integrity
Protection of trace evidence from loss or contamination is essential. In some instances, such as footwear or tire track impressions, the procedure used to collect the evidence is critical to the protection of its integrity. For example, special techniques are required to collect castings of impressions in snow. In regard to contamination, crime scene personnel must wear gloves when collecting evidence to prevent transfer of their DNA.
Special attention must be paid to items that will be processed for latent prints. These must be packaged and handled in a way that prevents the deposit of additional prints or smearing of evidence prints before visualization.
There are some cases where discussion between laboratory personnel is advised to determine the sequence of examination. For example, a firearm may be submitted to the laboratory with a request for latent print and DNA examination. Firearm examiners will need to ensure the weapon is safe for handling without compromising latent print and DNA evidence (per laboratory protocol). Some latent print visualization techniques can damage DNA, but latent print examiners would prefer to process the evidence before excessive handling takes place.
Physical evidence can be significantly degraded due to the effects of environmental factors before and/or after recovery.
The amount of evidentiary value is typically in inverse proportion to the duration and intensity of exposure to the following:
- Living organisms (bacteria, molds, insects, animals)
- Weather conditions (temperature, humidity, rain)
- The chemistry of a hostile environment (substrate at the location, soil pH)
- Superstrate (a covering of soil and its chemistry)
- The amount of time interacting with any or all of the above
Improper collection and preservation, inadequate storage conditions, or carelessness within a laboratory can be as destructive to physical evidence as years of exposure in the external environment.
Examples of degraded physical evidence within the field of firearms identification include the following:
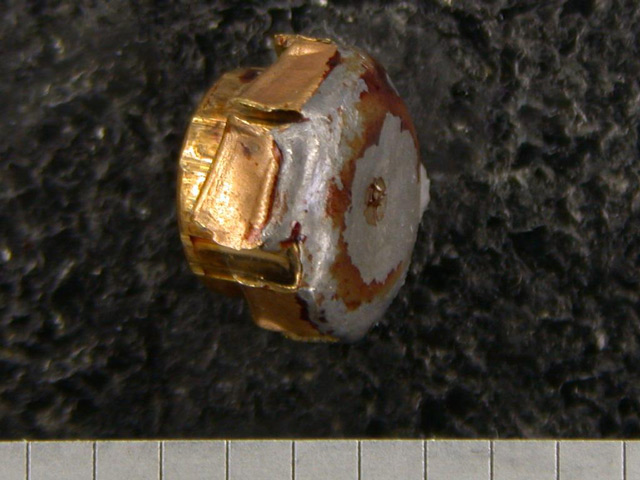
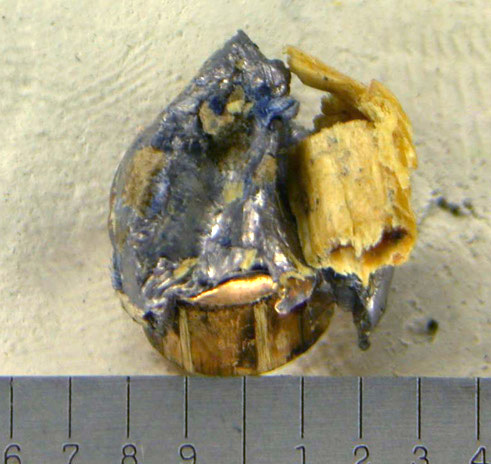
- A rusted firearm barrel (may preclude identification)
- Oxidation of a lead bullet in soil
- Oxidation of the surface of a jacketed bullet due to a lengthy exposure to human tissue
- Clothing exposed to weather (may result in leached patterns of gunshot residues)
Additional Online Courses
- What Every First Responding Officer Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Collecting DNA Evidence at Property Crime Scenes
- DNA – A Prosecutor’s Practice Notebook
- Crime Scene and DNA Basics
- Laboratory Safety Programs
- DNA Amplification
- Population Genetics and Statistics
- Non-STR DNA Markers: SNPs, Y-STRs, LCN and mtDNA
- Firearms Examiner Training
- Forensic DNA Education for Law Enforcement Decisionmakers
- What Every Investigator and Evidence Technician Should Know About DNA Evidence
- Principles of Forensic DNA for Officers of the Court
- Law 101: Legal Guide for the Forensic Expert
- Laboratory Orientation and Testing of Body Fluids and Tissues
- DNA Extraction and Quantitation
- STR Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Communication Skills, Report Writing, and Courtroom Testimony
- Español for Law Enforcement
- Amplified DNA Product Separation for Forensic Analysts